Safety Precautions
Always wear protective gear, including a helmet, gloves, and safety glasses, when operating a chainsaw. Ensure proper footing and avoid kickback by using reduced kickback chains. Follow all safety guidelines in the manual to minimize risks and ensure safe operation.
1.1 Essential Safety Gear
Protective equipment is crucial when operating a chainsaw. Always wear a helmet with a face shield or safety glasses to guard against debris. Ear protection, such as earplugs or mufflers, is essential to prevent hearing damage. Gloves provide grip and protect hands from cuts or abrasions. Wear chainsaw chaps or sturdy pants made of cut-resistant material to protect legs from accidental cuts. Steel-toe boots with good traction ensure stability while working. Ensure all gear fits properly and remains secure during operation. Using genuine replacement parts, as recommended by manufacturers like STIHL, ensures compatibility and safety. Proper safety gear minimizes risks and ensures safe chainsaw operation. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for protective equipment to maintain optimal safety.
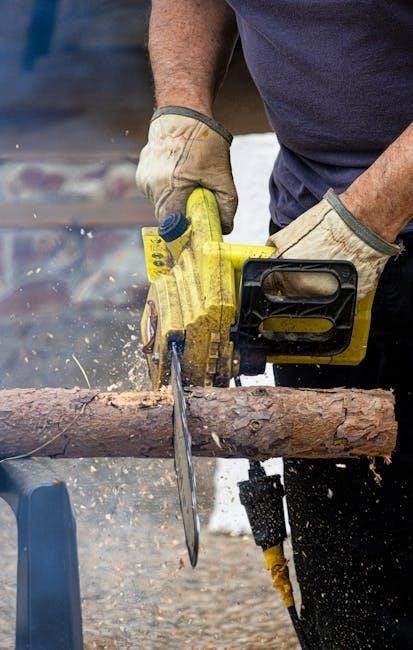

1.2 Understanding Kickback and Prevention
Kickback is a sudden, uncontrollable movement of the chainsaw that can occur when the chain catches on an object or when cutting improperly. It is a major safety hazard and can lead to serious injury. To prevent kickback, use chainsaws equipped with safety features such as reduced kickback bars and chains. These components are specifically designed to minimize the risk of kickback. Always maintain a firm grip on the saw with both hands and ensure proper footing. Avoid cutting near the upper portion of the guide bar, as this is the most common kickback zone; Keep the chain sharp and properly tensioned, as a dull or loose chain increases the risk of kickback. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for chain type and bar length. Regular maintenance and proper cutting techniques are essential to reduce kickback risks and ensure safe operation.
1.3 Safe Operating Environments
Ensure the operating area is clean, well-lit, and free from obstacles or tripping hazards. Always operate the chainsaw in a stable, open environment with good ventilation to avoid inhaling harmful fumes. Avoid cutting in confined or poorly ventilated spaces. Keep bystanders, children, and pets at a safe distance. Never use the chainsaw in wet or slippery conditions, as this can increase the risk of accidents. Maintain a firm stance and avoid reaching or stretching while cutting. Operate the chainsaw only when you are physically fit and not under the influence of medications or substances that could impair your ability. Be aware of your surroundings, including overhead obstacles, power lines, and uneven terrain. Always follow local safety regulations and guidelines for chainsaw operation in public or shared spaces.
Chainsaw Components
A chainsaw consists of key parts like the engine, bar, chain, handle, and safety features such as a chain brake and kickback mechanism. These components work together to ensure efficient cutting and user safety.
2.1 Key Parts of a Chainsaw
A chainsaw is made up of several essential components that ensure its functionality and safety. The engine, either gas-powered or electric, provides the power needed to operate the saw. The bar, which is the metal guide, and the chain, with its cutting teeth, work together to cut through wood. The handle, often equipped with anti-vibration features, allows for comfortable grip and control. Safety features like the chain brake and kickback mechanism are critical to prevent accidents. Additional components include the muffler to reduce noise, the air filter for engine protection, and the oil system to lubricate the chain. Understanding these parts is crucial for proper operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the chainsaw runs efficiently and safely.
2.2 Types of Chainsaws
Chainsaws are available in various types to suit different needs and applications. Gas-powered chainsaws are the most common, offering high power and portability, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks like felling large trees. Electric chainsaws are quieter, lighter, and suitable for smaller jobs, such as pruning or cutting firewood, with the added convenience of minimal maintenance. Battery-powered chainsaws provide cordless operation, combining the benefits of electric and gas models, and are perfect for environmentally friendly use. Pole saws are specialized for cutting high branches, featuring extended handles with a chainsaw attachment. Additionally, there are manual and hydraulic chainsaws designed for specific industrial or niche applications. Each type has unique features, catering to different user preferences, work environments, and task requirements.
2.3 Bar and Chain Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the bar and chain is crucial for optimal chainsaw performance and longevity. Always clean the bar and chain after use to remove debris and resin, which can impede proper function. Sharpen the chain frequently using a file or sharpening tool, ensuring consistent cutter and raker angles. Proper chain tension is essential; refer to the manual for specific adjustment procedures. Lubricate the bar and chain regularly with high-quality bar oil to reduce friction and prevent overheating. Inspect the chain for wear or damage, replacing it when necessary. Store the chainsaw with the chain off the bar to avoid rust and corrosion. Proper maintenance ensures smooth operation, enhances cutting efficiency, and extends the lifespan of your chainsaw. Neglecting these steps can lead to poor performance, increased wear, and potential safety hazards.
Operating the Chainsaw
Ensure proper footing, start the chainsaw on a flat surface, and maintain a firm grip with both hands. Always follow starting procedures and cutting techniques outlined in the manual to ensure safe and efficient operation.
3.1 Starting Procedures
Starting a chainsaw safely and correctly is essential to ensure proper operation and minimize risks. Always begin by reading the operator’s manual for specific instructions, as procedures may vary by model. Ensure the chain brake is engaged and the chainsaw is placed on a flat, stable surface. Wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves, safety glasses, and a helmet. Prime the engine by pressing the primer bulb 2-3 times until fuel flows into the bulb. Move the choke to the “start” position and pull the starter cord gently until resistance is felt, then pull sharply. Once the engine coughs, move the choke to the “run” position and allow the chainsaw to warm up. Never start the chainsaw near open flames or sparks, and ensure the area is clear of debris. Always maintain a firm grip with both hands and proper footing. Failure to follow these steps can lead to accidents or engine damage. Ensure the chain is not touching any surfaces when starting. If the chainsaw does not start after a few attempts, refer to the troubleshooting section in the manual.
3.2 Basic Cutting Techniques
Mastering basic cutting techniques is crucial for safe and efficient chainsaw use. Always maintain a firm, two-handed grip on the saw, with your left hand on the front handle and your right hand on the rear handle. Stand with a stable stance, feet shoulder-width apart, and ensure the area is clear of obstacles. Plan your cut by identifying the direction of the fall and making a horizontal cut on the underside of the branch or trunk. For horizontal cuts, use a slight upward angle to prevent the saw from binding. Apply steady, controlled pressure, allowing the chain to do the work without forcing it. Avoid excessive pressure, as this can cause loss of control or kickback. For thicker logs, make a “score” cut on the top and a “release” cut from the bottom, meeting the score cut in the center. Always cut on the pull stroke, as this provides better control and reduces the risk of accidents. Keep the chain sharp, as a dull chain increases effort and the likelihood of kickback. Regularly inspect the work area for hazards and ensure proper lighting. Never cut overhead or in tight spaces without proper training. Always follow the specific cutting techniques outlined in your chainsaw’s manual for optimal performance and safety.
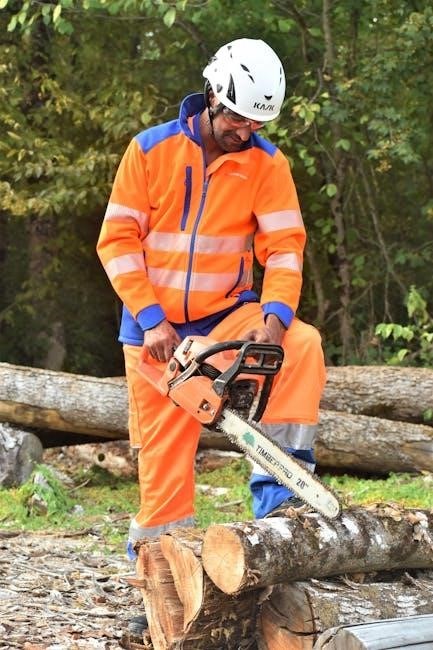

Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regularly sharpen the chain, check bar oil levels, and clean the air filter to ensure optimal performance. Address issues like dull chains or faulty ignition promptly to avoid downtime.
4.1 Routine Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring your chainsaw operates efficiently and safely. Start by checking the chain tension daily, as a loose chain can cause accidents, while an overly tight chain may damage the bar. Lubricate the chain frequently to prevent rust and wear, using the recommended bar oil. Sharpen the chain regularly to maintain cutting performance, and clean the air filter to ensure proper engine airflow. Inspect the spark plug and replace it as needed to avoid ignition issues. Additionally, monitor the oil levels for both the engine and the bar, refilling as necessary. Clean the chainsaw thoroughly after each use to remove debris and sap, which can hinder performance. Store the chainsaw in a dry place, disengaged and with a protective cover, to prevent rust and accidental starts. By following these routine tasks, you can extend the lifespan of your chainsaw and ensure optimal functionality.

4.2 Common Issues and Solutions
Common chainsaw issues often arise from poor maintenance or improper use. A dull chain can cause slow cutting and increased vibration, so sharpen or replace it as needed. If the chainsaw is difficult to start, check the spark plug for fouling or improper gap, and ensure the air filter is clean. A loose chain can lead to kickback hazards, so always tighten it before use. If the engine stalls, inspect the fuel line for blockages or leaks and ensure the correct fuel mixture is used. Chainsaw overheating can occur from a clogged cooling system; clean the fins regularly. For poor cutting performance, check the chain tension and alignment. Lubrication issues, such as dry bars, can damage the chain and bar; always use recommended bar oil. Addressing these common problems promptly ensures reliable operation and extends the chainsaw’s lifespan.

Storage and Transportation
Store the chainsaw in a dry place, disconnected from the spark plug. Clean thoroughly before storage. Transport in a suitable carrier or case to ensure safety and protection.
5.1 Proper Storage Conditions
To maintain your chainsaw’s performance and longevity, store it in a dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and moisture. Ensure the storage location is secure and out of reach of children; Before storing, clean the chainsaw thoroughly, removing any debris or sap from the bar and chain. Drain the fuel tank or use a fuel stabilizer to prevent corrosion. Disconnect the spark plug to avoid accidental startups. Store the chain in a protective case or cover to prevent rust. Keep the operator’s manual with the chainsaw for easy reference. Regularly inspect stored components for damage or wear. Proper storage ensures safety, prevents deterioration, and guarantees the chainsaw is ready for its next use.
5.2 Safe Transportation Methods
When transporting a chainsaw, always ensure it is securely fastened to prevent movement during transit. Use a sturdy, protective case or cover to safeguard the bar and chain from damage. Disconnect the spark plug to avoid accidental startups and drain the fuel tank to reduce fire hazards. Wear protective gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, even during transport. Keep the chainsaw out of reach of children and pets. Avoid transporting loose chains or accessories separately, as they may cause injury or get lost. Ensure the vehicle is well-ventilated to prevent fuel fumes buildup. Follow local regulations for transporting power tools. By taking these precautions, you can ensure safe and secure transportation of your chainsaw, protecting both the tool and others involved.



About the author